Managing Metadata Fields
Metadata fields allow you to attach custom information to experiments and feature flags. Before you can add metadata to experiments or flags, you need to create metadata field definitions that define what types of custom information can be tracked.
What are Metadata Fields?
Metadata fields are custom field definitions that can be attached to experiments and feature flags. They help you organize and track additional context about your experiments and flags, such as:
- Product area or team ownership
- Business objectives or goals
- Launch dates or milestones
- Compliance or regulatory requirements
Accessing Metadata Field Management
To manage metadata fields, navigate to your workspace settings and select the Metadata tab.
Creating a New Metadata Field
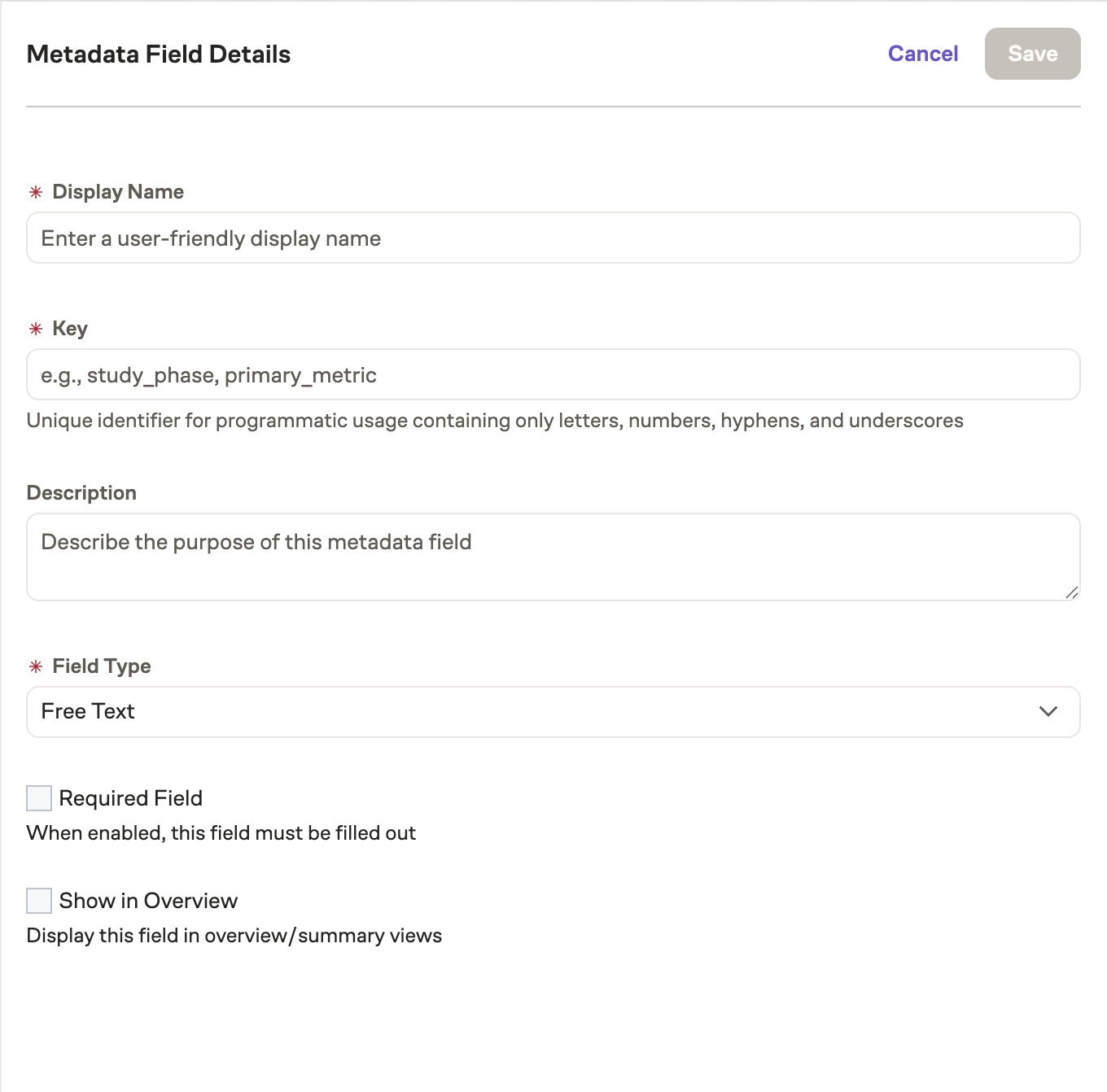
Click Add Metadata Field to open the creation form:
Field Properties
When creating a metadata field, you'll configure the following properties:
Display Name
The human-readable name shown in the UI. This should be clear and descriptive (max 200 characters).
Key
A unique identifier for the field used in the API. The key is automatically generated from the display name but can be customized. Keys must:
- Be unique within your workspace
- Contain only alphanumeric characters, hyphens, and underscores
- Not use reserved words
Description
An optional explanation of what this field is for and how it should be used (max 1000 characters).
Field Type
Metadata fields support two types:
Freetext
- Allows open-ended text input
- Supports up to 10,000 characters
- Ideal for descriptions, notes, or URLs
Select (Dropdown)
- Provides a dropdown with predefined options
- Supports single-select or multi-select
- Can have 1-100 predefined values
- Ideal for categories, teams, or standardized values
Additional Options
- Multi-select (Select only): Allow users to select multiple values from the dropdown
- Required: Make this field mandatory when creating or editing experiments/flags
- Show in Overview: Display this field in experiment overview
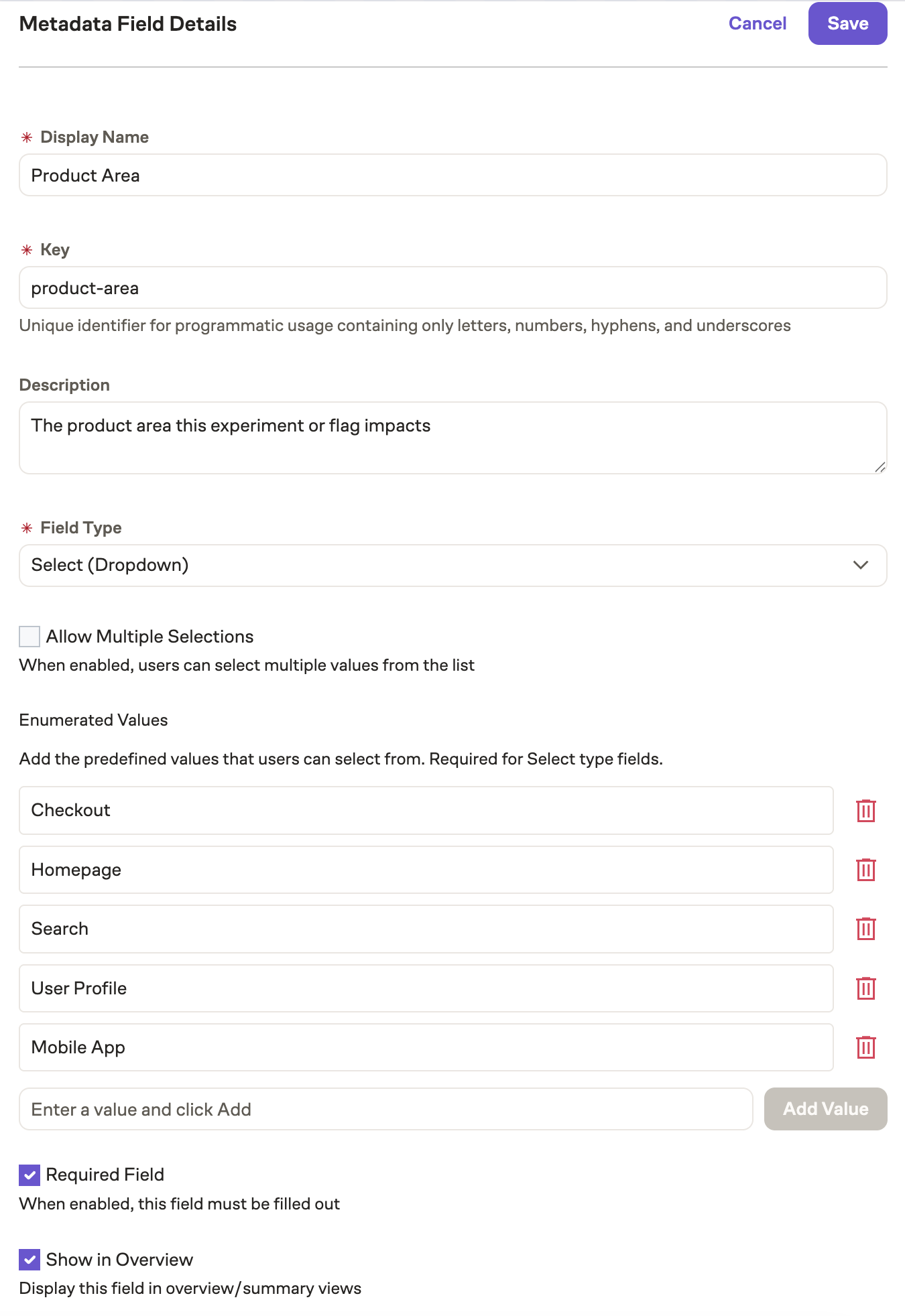
Example: Creating a Product Area Field
A common use case is tracking which product area an experiment or flag affects:
- Display Name:
Product Area - Key:
product_area(auto-generated) - Description:
The product area this experiment or flag impacts - Field Type:
Select (Dropdown) - Multi-select:
No - Required:
Yes - Show in Overview:
Yes - Enumerated Values:
Checkout,Homepage,Search,User Profile,Mobile App
Managing Enumerated Values
For Select type fields, you can manage the list of available values.
Adding Enumerated Values
When creating an enumerated field, add values in the Enumerated Values section. Each value should be a distinct option that users can select.
Editing Enumerated Values
To edit an existing enumerated value:
- Click on the metadata field in the list
- Find the enumerated value you want to edit
- Click the edit icon
- Update the value text
- Save your changes
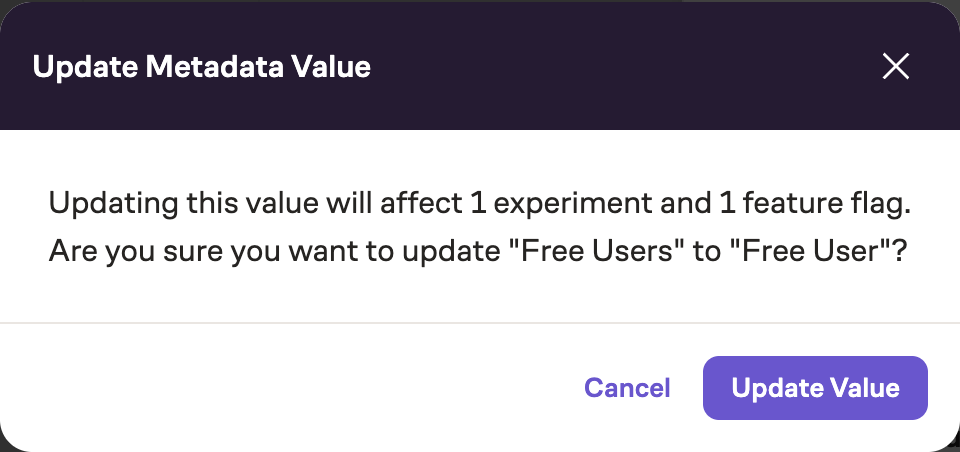
Updating an enumerated value will change it everywhere it's currently used. If you want to track usage before and after the change separately, consider creating a new value instead.
When trying to change an enumerated value that is in use, the following modal will pop up warning the user of this action and its consequences:
Deleting Enumerated Values
To delete an enumerated value:
- Click on the metadata field in the list
- Find the enumerated value you want to delete
- Click the delete icon
- Confirm the deletion
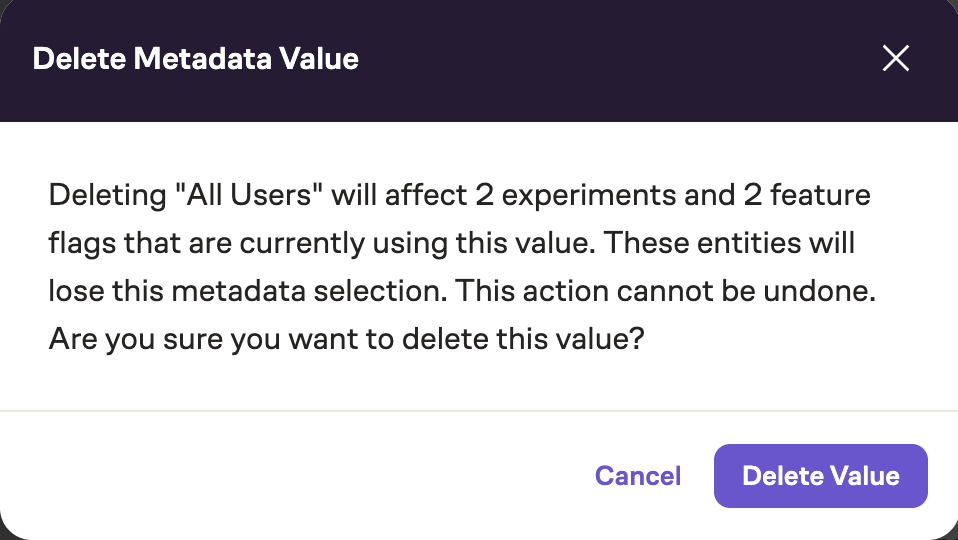
Deleting an enumerated value will remove it from any experiments or flags currently using it. Check the usage count before deleting.
When trying to delete an enumerated value that is in use, the following modal will pop up warning the user of this action and its consequences:
Editing Metadata Fields
To edit an existing metadata field:
- Click on the field in the list
- The field details sidebar will open
- Modify the properties you want to change
- Save your changes
You cannot change the field type (Freetext to Enum or vice versa) after creation. If you need to change the type, you'll need to create a new field.
Viewing Field Usage
The field details sidebar shows usage counts for both experiments and feature flags. This helps you understand how widely a field is being used before making changes or deleting it.
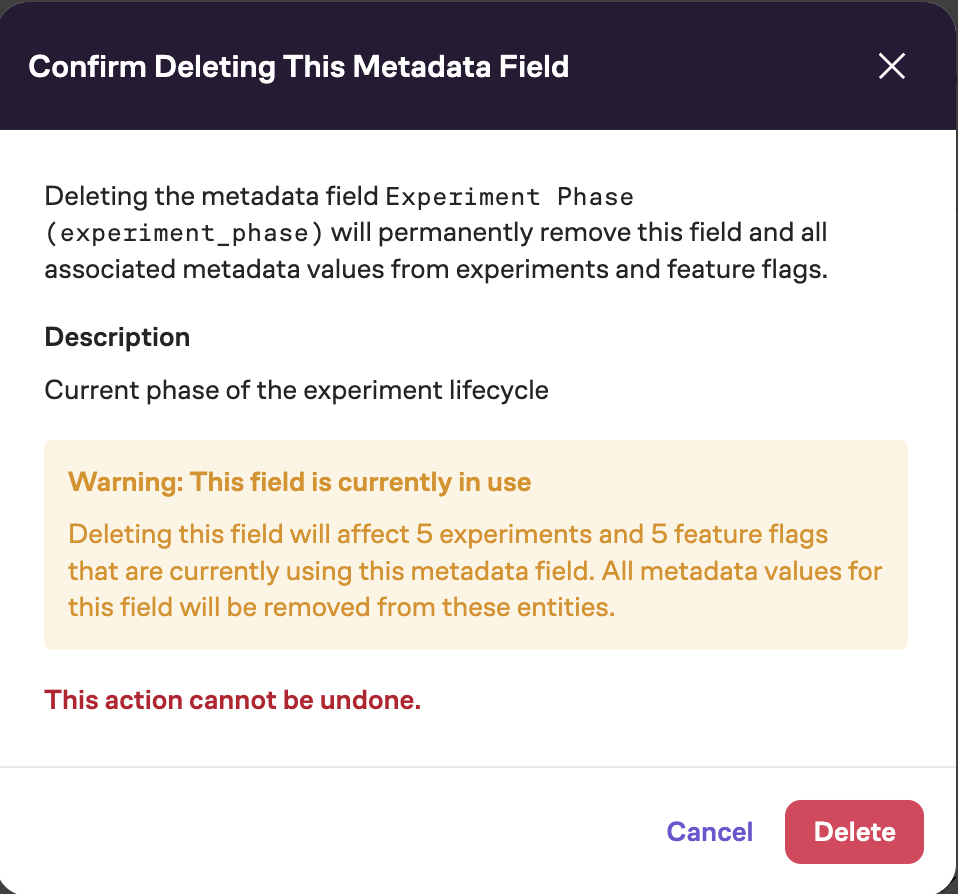
Deleting Metadata Fields
To delete a metadata field:
- Click on the field in the list
- Click Delete Field
- Review the usage counts in the confirmation dialog
- Confirm the deletion
Deleting a metadata field will remove all data associated with that field from all experiments and flags. This action cannot be undone.
When trying to delete a metadata field that is in use, the following modal will pop up warning the user of this action and its consequences:
Filtering and Sorting
The metadata fields list supports:
- Search: Filter fields by display name or key
- Sorting: Sort by display name, key, field type, required status, or show in overview status
- Pagination: Navigate through large numbers of fields
Best Practices
Start Simple
Begin with a few essential fields that provide the most value. You can always add more fields later as needs evolve.
Use Enum Fields for Standardization
When possible, use enum fields instead of freetext to ensure consistent data entry and enable better filtering and reporting.
Make Strategic Fields Required
Only mark fields as required if they're truly essential. Too many required fields can slow down the workflow for creating experiments and flags.
Enable Show in Overview for Key Information
Use the "Show in Overview" option for fields that provide at-a-glance value in list views, but be selective to avoid cluttering the interface.
Document Field Purposes
Use the description field to clearly explain what each metadata field is for and how it should be used. This helps ensure consistent usage across your team.