Connecting Redshift
Preparing your Warehouse for Eppo
Before you connect Eppo to your data warehouse, it is recommended that you create a User for Eppo. This User should then be used to connect Eppo to your warehouse. Additionally, this User will need to be granted read access to tables from which you'd like Eppo to query SQL definitions from.
1. Add Eppo IP Address to Allowlist
For Eppo to connect to your Redshift database, you’ll need to allow our inbound IP addresses in your Cluster’s Security Group settings:
- Log in to the Redshift Management Console.
- Select Clusters from the left sidebar then select the cluster you want to connect to Eppo.
- From the Cluster Details page, navigate to the Properties tab and scroll to the Network and Security section.
- Under VPC Security Groups, click the Security Group you want to use to allow communication from Eppo.
- Click the Inbound Rules tab at the bottom of the page then click Edit.
- Click Add Rule to add a new Inbound Rule. a. Set the Type to Redshift. b. Adjust the Port, if needed. c. Enter the following into the Source field:
| IP Address |
|---|
34.133.196.109 |
35.226.89.62 |
34.41.172.201 |
34.29.62.236 |
34.132.152.78 |
35.232.0.89 |
34.41.154.239 |
146.148.74.70 |
34.121.71.161 |
34.70.156.102 |
35.239.118.244 |
34.132.46.38 |
35.238.158.100 |
34.42.48.99 |
34.134.43.217 |
34.134.2.209 |
34.134.152.212 |
35.225.36.104 |
34.31.169.195 |
34.134.214.137 |
34.30.65.165 |
34.28.215.125 |
35.193.17.22 |
34.27.118.169 |
- Click Save.
2. Create Dedicated User for Eppo
You should create a new user and grant SELECT permissions to the tables the user (i.e., Eppo) will access.
-
Go back to the Redshift console and connect the query editor to your data source.
-
Create a user with the query below, replacing
<password>with a unique, secure password.Note: The password must contain at least one uppercase, one lowercase, and one numeric character.
CREATE USER eppo_user WITH PASSWORD '<password>' SYSLOG ACCESS RESTRICTED;
- Grant this user the appropriate privileges for any tables we will need to access. This generally includes your assignment or exposure events, fact tables from which your metrics are derived, and dimension tables that you commonly use in your analyses.
You can do so by running the following commands, replacing <schema_name> with the name of your schema.
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA <schema_name> TO eppo_user;`
`GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA <schema_name> TO eppo_user;
If you’d like to grant SELECT permissions on a table-by-table basis, you can run the query below to generate the queries to GRANT SELECT ON each table in a schema. You’ll then need to exclude any grant statements for tables that you don’t want the user to access.
GRANT SELECT ON TABLE <schema>.<table1> TO ROLE eppo_user;
GRANT SELECT ON TABLE <schema>.<table2> TO ROLE eppo_user;
NOTE: The AWS Redshift query editor will not run multi-statement queries; it’s recommended you use SQL Workbench to connect to Redshift and run multiple queries at one time.
- Create a schema for Eppo to write intermediate results and temporary tables.
CREATE SCHEMA IF NOT EXISTS eppo_output;
GRANT ALL ON SCHEMA eppo_output TO eppo_user;
3. Gather Redshift Connection Details
You'll want to gather the following connection details from Redshift:
-
Endpoint: The endpoint of your Redshift cluster database
Go to the Properties tab of your Redshift Cluster Details page.
Under the Connection details section, copy the Endpoint up to but not including the colon (:).
-
Database Port: default port number for Redshift is 5439
From your Redshift Cluster Details page, you can find the port number under the Database configurations section of the Properties tab.
-
Database Name: name of your Redshift database
You can also find your Database Name under the Database configurations section of the Properties tab.
(Optional) Event tracking
To use Eppo's Event Tracking with Redshift, additional configuration is required:
-
S3 Bucket: Eppo will write events to this bucket before bulk inserting into Redshift.
Files will be automatically deleted from this bucket after insertion into Redshift.
-
AWS Region: The region the Redshift cluster resides in
-
Access Key ID: Credentials of the service account Eppo can use to upload files to the S3 bucket
-
Secret Access Key: Credentials of the service account Eppo can use to upload files to the S3 bucket
-
AWS IAM Role: IAM role to use when running
COPY INTOoperations to load data from S3 into the Redshift instance.This role needs permissions to
LISTand the contents of the above S3 bucket as well asGETobjects within the S3 bucket.
(Optional) SSH Tunnel
Eppo supports connecting to a Redshift cluster over an SSH tunnel.
Connect with a username & password combination or public key option.
SSH tunnel with username and password
- tunnel host
- username & password
SSH tunnel with public key
- tunnel host
- username
- public key
Connecting your Warehouse to Eppo
Now that you have a proper User created for Eppo with adequate privileges, you can use it to connect Eppo to your warehouse.
Initial Configuration of Credentials
- Log in to your Eppo account at eppo.cloud
- Click the
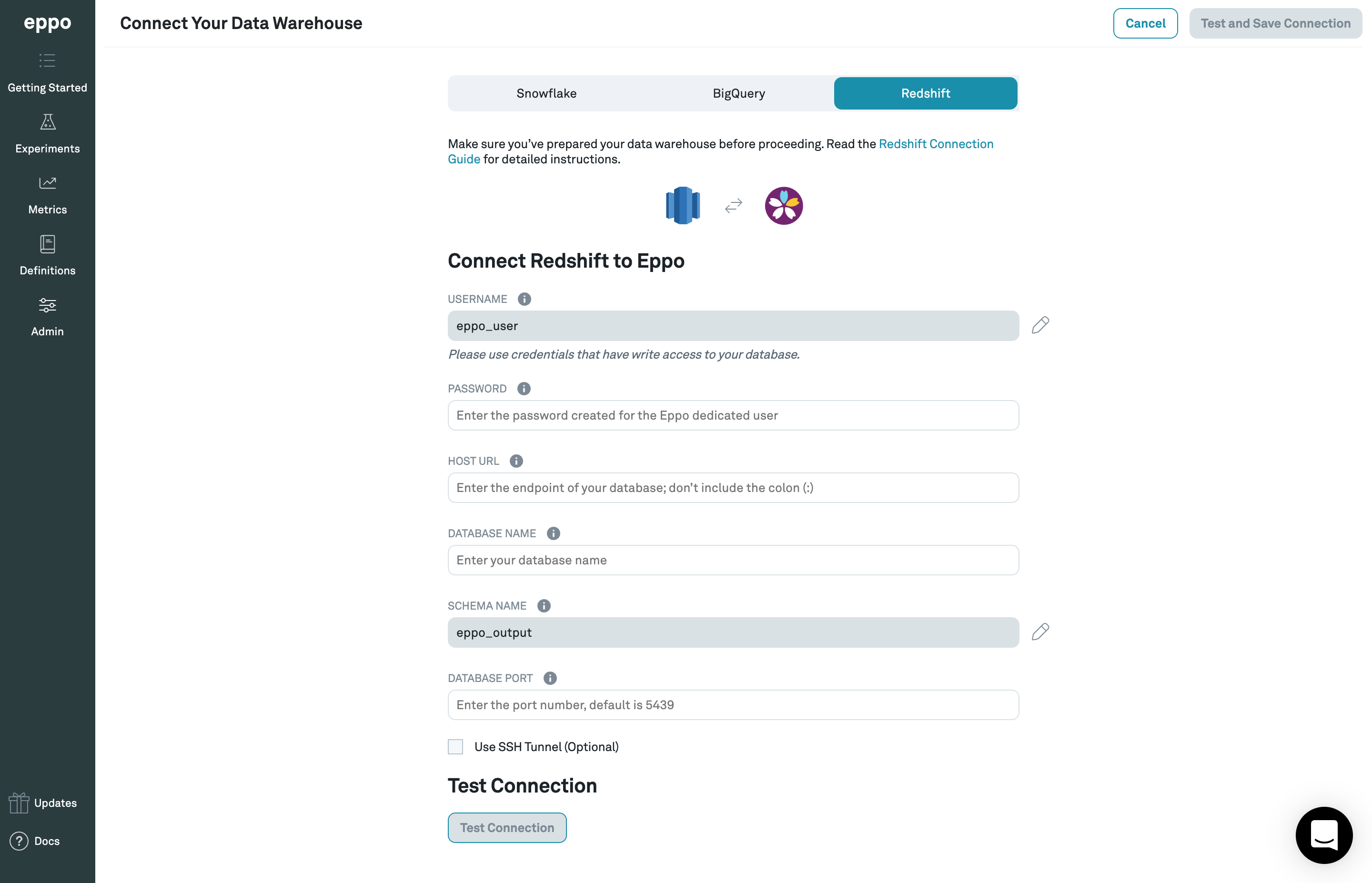
Getting Startedbutton in the top-right corner. Once on that screen, and within theConnect your Warehousetab, click theConnect your data warehouse to Eppobutton in the bottom right-hand corner of the screen. - Once on the data warehouse connection screen, click the
Redshifttab. From there, you should be prompted to enter all of the necessary information for doing so. This information includes:
- Connection type - Redshift
- User -
eppo_user - Password - the
<password>you chose - Host Url - Endpoint from previous section
- Database name - Database name from previous section
- Schema name -
eppo_output - Port - Database port from previous section
- [Optional] Event Tracking Configuration - values from previous section
- Enter the values into the form (which should look like the screenshot below), then click
Test Connection. Once this test succeeds, save your settings by clickingTest and Save Connection.
Note: Eppo uses Google Secret Manager to store and manage your credentials. Credentials are never stored in plaintext, and Secret Manager can only be accessed via authorized roles in GCP, where all usage is monitored and logged.
Updating Credentials
Credentials can be updated at any time within the Admin panel of the app.